USAID’s Early Grade Reading Program II solidified a sustainable foundation for improving children’s reading skills in Nepal
Objective
To improve early grade literacy in grades 1–3 for students in Nepali public schools.
Approach
The Early Grade Reading Program II (EGRP II) provided technical support to the Government of Nepal’s National Early Grade Reading Program (NEGRP), which aims to help children read with fluency and comprehension. NEGRP is led by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology with support from USAID and other development partners.
Impact
- As a result of EGRP II activities, the proportion of grade 3 students in the overall intervention who became fluent readers increased by 8 percentage points between baseline and endline.
- The COVID-19 response intervention also helped move students into higher reading proficiency levels between baseline and endline. For example, the proportion of emergent readers increased by 14 percentage points in grade 2 and by 11 percentage points in grade 3.
The two-year (2020-2022) Early Grade Reading Program II (EGRP II) was a partnership between the Government of Nepal and the U.S. Agency for International Development that helped children across Nepal learn to read with fluency and comprehension, skills that help set them up for success later in life.
EGRP II built on the Early Grade Reading Program (EGRP), led by RTI from 2015–2020, which also achieved significant impact in terms of reading gains. EGRP II continued creating the climate conducive to scaling up early grade reading activities initiated under EGRP.
EGRP II activities included:
- Supporting development and rollout of the Integrated Curriculum and continuing to scale up the government’s National Early Grade Reading Program (NEGRP).
- Building municipal- and provincial-level capacity for delivering early grade reading services.
- Improving local governments’ ability to provide effective teacher professional support.
- Supporting continuity of learning in response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
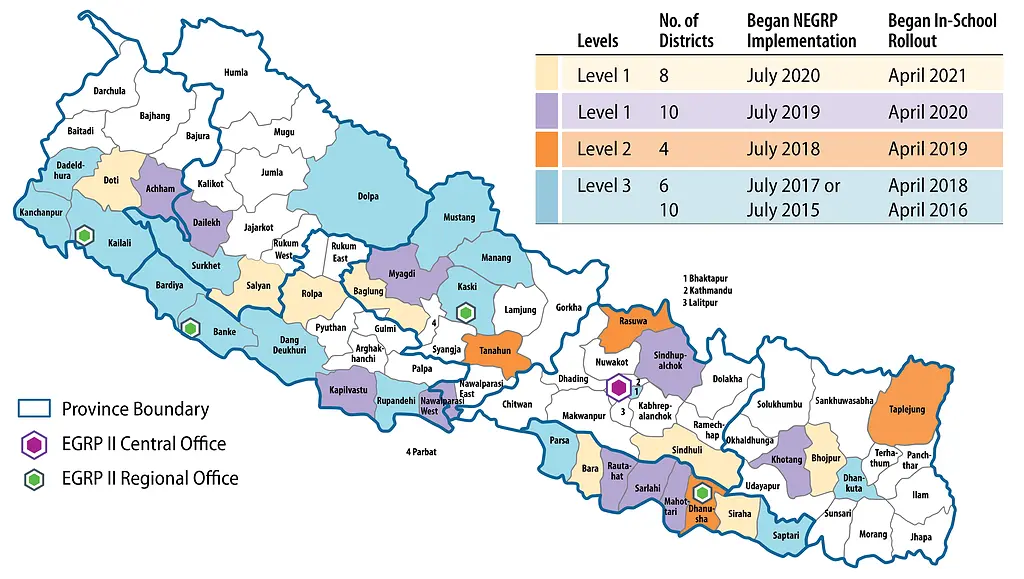
These activities reached 396 local governments (referred to as “municipalities” or “rural municipalities” in Nepali) in 38 NEGRP target districts across all 7 of Nepal’s provinces.
Improving Teacher Training, Instruction, and Support
Providing support and training for teachers is a critical step in ensuring students receive a quality education. EGRP II assisted the government to integrate early grade reading best practices in their Integrated Curriculum and roll out trainings and orientations on these practices at central and cluster levels. Training topics included:
- key reading components and instructional approaches
- best practices for teaching Nepali to second language (L2) learners
- the “I do, we do, you do” gradual-release instructional model (where teachers first illustrate a skill, practice the skill with their students, and then have the students perform it), and
- best practices for using instructional materials, such as teacher guides and student workbooks and supplementary reading materials at various reading levels and in several languages.
EGRP II supported rollout of comprehensive teacher professional development master trainings on the Integrated Curriculum. In total over 200 trainees were trained and training resource materials covering all subjects in grades 1–3 were created and distributed. EGRP II also helped the government develop a quality assurance tool to ensure consistency of trainings as they are cascaded from the master trainer level to lower levels.

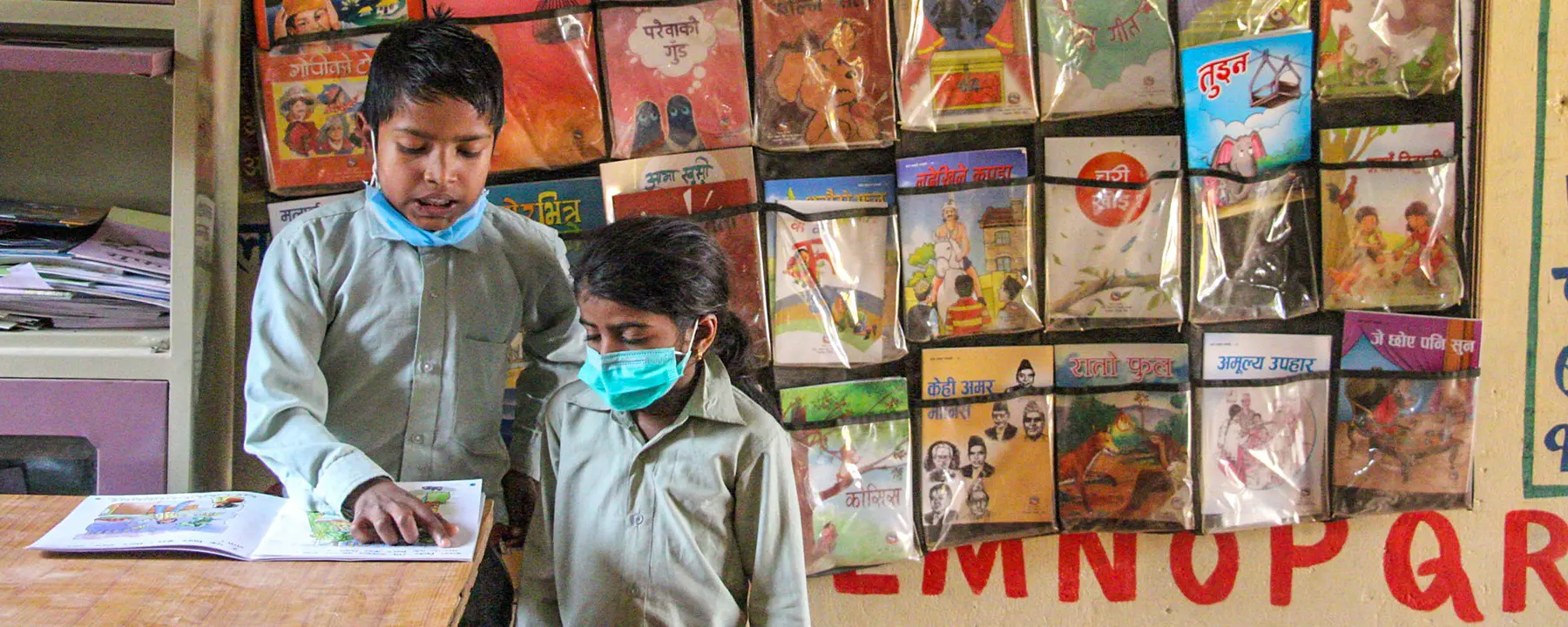
A teacher works with students using teaching and learning materials provided by EGRP II. Photo by Avash Karmacharya
In addition to training, ongoing support to teachers, including mentoring and coaching, is essential to ensure that what is learned is being applied in the classroom. Working with Nepal’s Center for Education and Human Resource Development (CEHRD), EGPR II helped to revise and roll out a teacher professional support (TPS) system to operationalize the new curriculum and materials. This system provided local governments with a menu of teacher support options that they can select based on their local context and resources.

Building Capacity to Scale Up Early Grade Reading
As with EGRP, all EGRP II’s activities were designed to foster sustainability through government ownership of program implementation and coordination across all levels of the education system (local, district, and provincial).
Through capacity building workshops, EGRP II continued to engage and build stakeholder knowledge and skills in early grade reading concepts; NEGRP goals, strategies, and activities; and the roles and responsibilities of each education system level in reaching early grade reading goals.
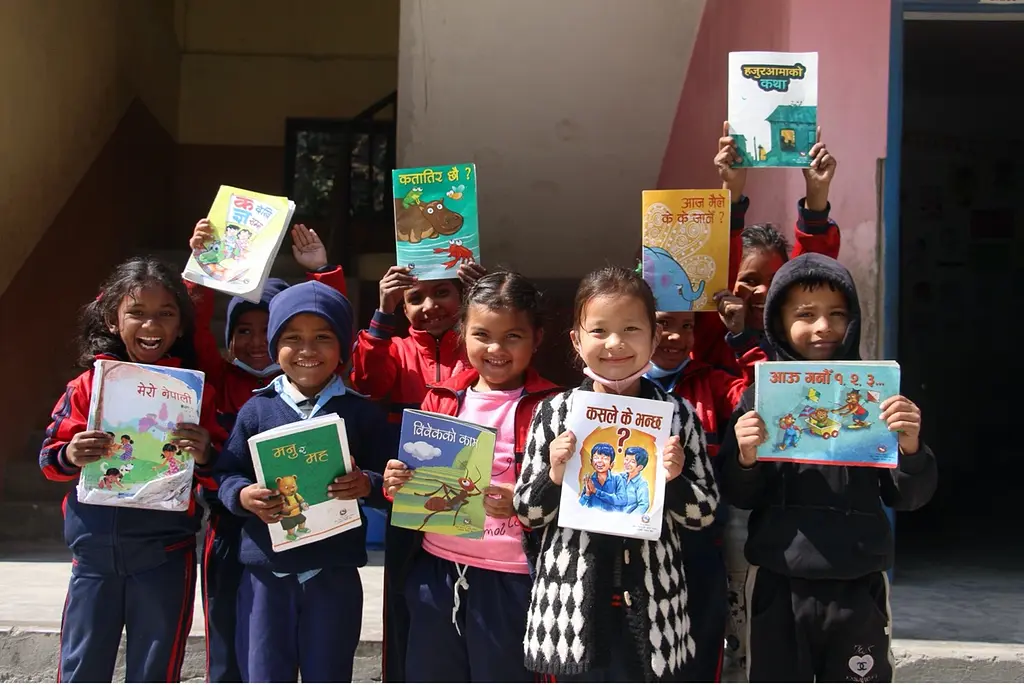

Children show off their supplementary reading materials distributed with EGRP II support. Photo by Avash Karmacharya
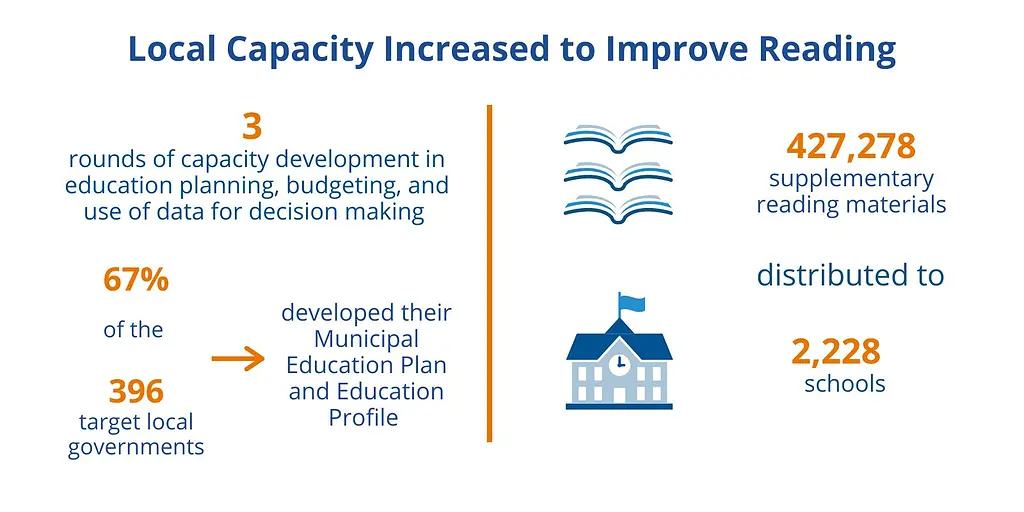
Importantly, the program also helped integrate NEGRP interventions into local level policies and programs across 396 target local governments by supporting officials with planning and budgeting. Training on preparing Municipal Education Plans in consultation with local stakeholders succeeded in helping local governments allocate their own resources to early grade reading activities, including support and coaching for teachers.
EGRP II also assisted selected local governments to distribute supplementary reading materials to schools to promote students’ love of reading.
Ensuring Learning Continuity in Response to the COVID-19 Pandemic
As the pandemic forced school closures, flexible learning approaches—such as home-based schooling supported by parents and teachers—and use of information technology became critical to ensure continuity of learning.
At the local level, EGRP II disseminated government COVID-19 response guidelines for the education sector, including flexible learning approaches, a school reopening framework, and guidelines for facilitating home-based schooling created with inputs from EGRP II team members.
In terms of use of information technology, EGRP II partner organization Open Learning Exchange Nepal (OLE Nepal) developed 119 new digital interactive lessons for grades 1–3, for Nepali, mathematics, science, social studies, English, Nepali Sign Language, and for children with dyslexia, now uploaded in CEHRD’s online learning portal. OLE Nepal—a social benefit organization established in 2007 with the vision of improving the quality of education and reducing the disparity in access to quality learning resources—has been partnering with the Government of Nepal to use technology to enhance the teaching-learning process in classrooms. OLE has provided this support through design, development, and distribution of curriculum-based interactive digital learning materials; teacher training on integrating digital content in daily lessons; setting up technology infrastructure in schools; and developing local capacity and awareness on effective use of technology.
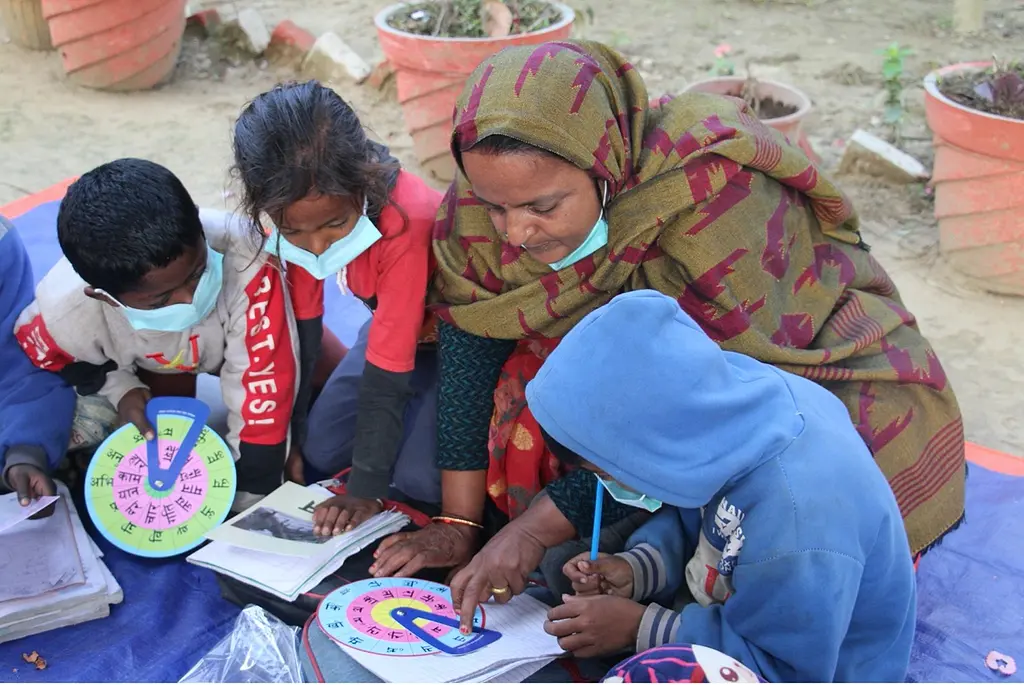
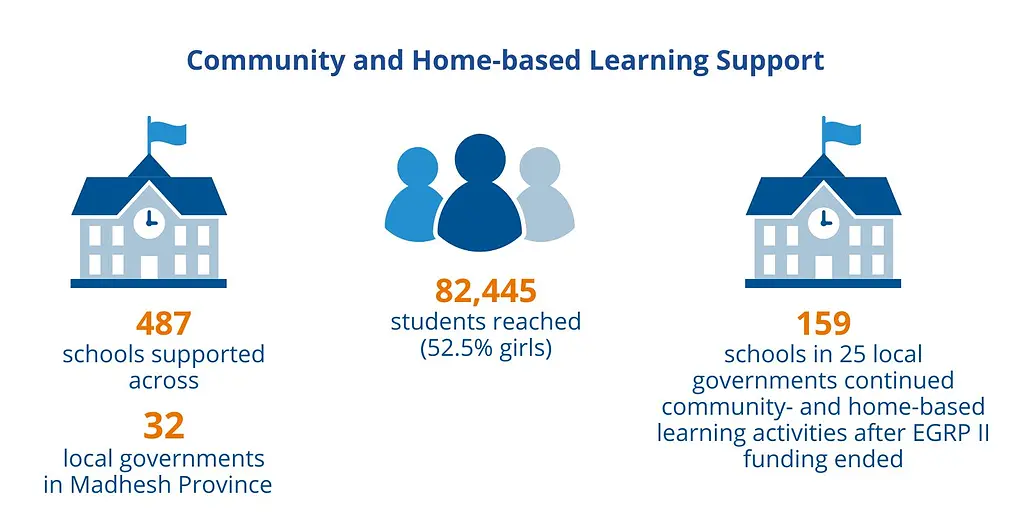
Additionally, EGRP II provided direct support to local education units to implement community- and home-based learning, targeting 32 rural, disadvantaged municipalities in Madhesh Province that were heavily impacted by COVID-19. These interventions included teacher training on flexible learning approaches, distribution of 2,156 tablets pre-loaded with offline learning content, and provision of decodable books and stationery packs.
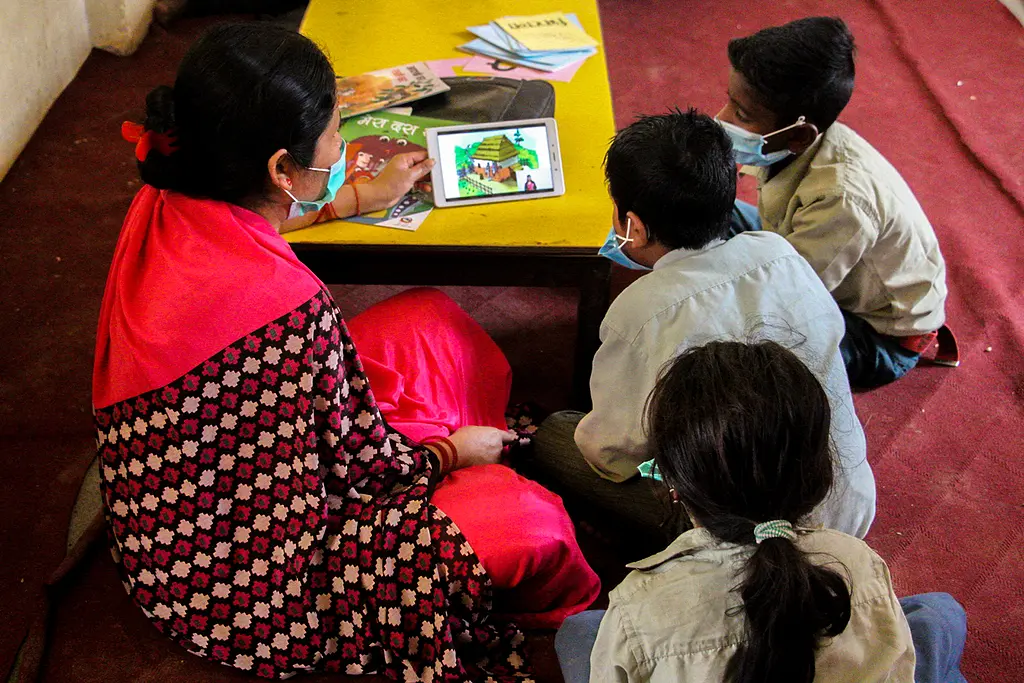

Students view educational content via tablets provided by EGRP II. Photo by Avash Karmacharya
The program’s catch-up learning activities at home and in the community also contributed to positive change for children whose learning was acutely affected by COVID-19 school closures. Through strengthened policy, practice, and system capacity, EGRP II made lasting contributions to improving early grade reading for learners across Nepal.
By the end of two years, EGRP II had supported the Government of Nepal to roll out early grade reading best practices and teacher professional support nationwide through the integrated curriculum; strengthened policy formulation and data analysis around children’s learning outcomes in early primary school; and built capacity of local governments for early grade reading service delivery.
- U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)
- Open Learning Exchange Nepal (OLE Nepal)


