
Lessons from the Better Health Programme Malaysia
Community engagement has proven an effective strategy to prevent and combat noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) in lower and middle-income countries (LMICs), particularly in prevention, control and support for NCDs such as tobacco cessation, blood pressure, diabetes control and psychosocial support for mental health. In Malaysia, the government has adopted community engagement as a key strategy in achieving its NCD objectives.
However, the COVID-19 pandemic has hindered community engagement approaches, which are typically conducted in-person. Amid government restrictions on in-person meetings, the Better Health Programme Malaysia, implemented by RTI with funding from the UK Foreign Commonwealth Development Office (FCDO), pivoted its approach to create and sustain a digital community around obesity and NCD prevention with the support of community health volunteers (CHVs).
Here are some of our key takeaways from building and sustaining this thriving virtual community during the pandemic.
1. Determine the best digital platforms using community-centered design
The Better Health Programme Malaysia was originally designed as a locally driven, community-based health intervention to prevent obesity and NCDs in urban poor communities from three public housing schemes (known as Kawasan Rukun Tetangga or KRT) around Kuala Lumpur. It engaged and leveraged CHVs to support community members in adopting positive behavioral modification for NCD and obesity prevention through in-person engagement. Prior to COVID-19, one of the key principles underpinning the programme was community-centered design, and that has been critical in informing the approach we took to shifting our engagement activities online.
We worked to understand the digital literacy and levels of social media know-how of our community participants through a digital needs assessment with CHVs. As Facebook and WhatsApp appeared most widely used by our community members to communicate and share information with others in their social circles, we went to where they were, digitally. We created MYJomSihat (translated as Let’s Get Healthy), a Facebook group that brings together CHVs, community members from all KRTs, medical practitioners, and project team members.
Over time, this group has evolved to a space that our programme relies on to implement a series of virtual, fun, and innovative NCD and obesity-related health promotion activities as well as interact with the community. In this space, members not only share the changes they have made to their dietary and physical activity practices, but also actively engage in modifying the design of activities in the programme.

The water challenge poster encouraged participants to reduce sugar in their drinks.
2. Keep it simple
Approximately 70% of NCDs can be prevented by changing behaviors, such as eating a balanced diet and engaging in more physical activity. To encourage engagement, our virtual community content and activities are aligned to simple key messages such as: eat more fruits and vegetables and drink more water, reduce your sugar consumption, and move your body more.
These messages sound deceptively simple. However, encouraging incremental but sustainable changes has allowed our community members to focus on things that they can do daily instead of focusing on a final goal that they may feel is difficult to achieve. In July of this year, we ran a month-long “Rethink Your Drink” water challenge activity that encouraged community members to drink more water and reduce their intake of sugary drinks. As part of the challenge, participants were asked to periodically share photos of their water intake. Throughout the challenge, we shared infographics on the health benefits of drinking water as well as novel ways to flavor their drinks without sugar. While we had initially expected community members to only share photos of their water bottles, they raised the bar by experimenting with fruit infusions and expounding on the nutritional benefits of their chosen flavors. This sparked vibrant discussions among community members. Ultimately, keeping messages simple works as community members feel empowered to make feasible changes.
3. Make content engaging and relatable by focusing on current issues of concern
We kept our ear to the ground by asking our CHVs individually about their lived experience. From these conversations with CHVs, we found that many community members and their offline social network of family and friends were, or have been, battling COVID-19. Global research suggests that COVID-19 is particularly challenging for people living with NCDs. Currently, Malaysia’s daily case reports are trending upward as the country confronts the Delta variant. In a bid to heighten awareness and increase preparedness of our community members, we ran a series of virtual activities linking NCDs and COVID-19. One of these activities was a Facebook live webinar that brought together medical experts and CHVs in a discussion on the correlation between NCDs and COVID-19, tips on practicing healthier lifestyles for the prevention of NCDs and COVID-19, and dietary and exercise tips for recovering COVID-19 patients.
By understanding and responding to what the community cares about, we found that people were open to sharing their personal stories. In the days following the webinar, various community members shared their experiences battling COVID-19 and were met with an outpouring of support and well-wishes from others who did not even know them personally.
4. Ensure an inclusive and welcoming community
The programme participants comprise male and female community members who represent a diverse range of ages and life stages, as well as ethnic backgrounds such as Malay, Chinese, Indian, and Sikh, which are reflective of Malaysia’s multicultural society. We found it was very important to ensure the community is inclusive and welcoming to all, irrespective of ethnicities, ages, languages, or gender. We’ve taken care to build on the diverse lived experiences of this virtual community in different ways, such as by leveraging younger family members to assist less tech-savvy elders in connecting digitally. For participants without a Facebook account, we also help them stay connected by engaging them through WhatsApp and posting on their behalf. In terms of language inclusivity, we ensure that key NCD prevention information is written in both Malay and Chinese, conduct health talks in Malay and Mandarin, and have WhatsApp groups catering to speakers of different languages.
5. Understand the roles individuals play in their communities
Finally, understanding the roles our community members play within their families and social networks has also been integral in encouraging virtual engagement, as this guides the timing, interactivity, and messaging of our activities to maximize reach and engagement. For instance, our most active participants are females between the ages of forty and sixty, who shoulder caregiving and cooking responsibilities for young children in their multigenerational families. Participating online serves as their “me time,” which sees them sharing photos of their families’ meals. We capitalized on their influence in changing their families’ dietary intake by running healthy cooking demonstrations and sharing information encouraging them to make incremental changes in their cooking practices. Over time, there has been a shift towards healthier eating practices, as well as requests for recipes from one another. Members have also regularly invited others in their real-world communities to join the group, which signals the value derived from this virtual community.
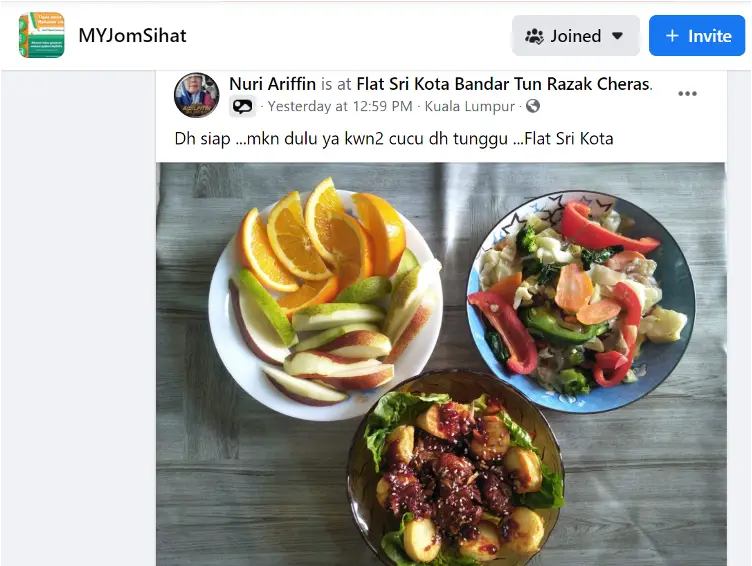
“Hi friends, food is ready. I’ll eat first – my grandkids are waiting.” A CHV shares her family’s lunch incorporating more fruits and vegetables in the MYJomSihat Facebook group.
Virtual community engagement has become crucial for obesity and NCD prevention in the face of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. To this end, the Better Health Programme Malaysia has created and sustained a thriving virtual community that encourages engagement by keeping messages simple, makes content relatable by tapping into trending issues at the heart of the community, and celebrates diversity and inclusion. By doing so, we hope to encourage sustainable behavior changes amongst our community members even in the absence of in-person peer support and encouragement, which will go a long way towards preventing obesity and NCD prevalence in low-resource Malaysian communities.



