Introduction
Individuals with substance use disorders and their families report challenges finding high-quality addiction treatment, as noted in recent Congressional hearings and by the media (Armstrong & Allen, 2017; Grassley, 2019). According to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) National Survey on Drug Use and Health, one in five adults who felt a need for addiction treatment but did not receive treatment said the reason was because they did not know where to get it (Park-Lee et al., 2017). For most health care provider types—hospitals, nursing homes, psychiatric hospitals, rehabilitation facilities, home health care, and hospice—the federal government sponsors online provider treatment locators that display quality measures for providers. For example, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS)’s Nursing Home Compare website allows the public to search for nursing homes and then compare them on structural quality measures like staff hours per resident and process and outcome measures drawn from inspection reports and clinical assessment data. Public-facing quality measures can drive quality improvements. CMS determined that performance improved on 60 percent of its 226 quality measures over 3 years (CMS, 2018).
SAMHSA hosts the Behavioral Health Treatment Locator to help consumers find behavioral health treatment (SAMHSA, 2020a). The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) hosts the NIAAA Alcohol Treatment Navigator to help consumers find treatment for alcohol use disorders (NIAAA, 2020). Both websites use the SAMHSA Inventory of Behavioral Health Services (I-BHS) and direct input from states and providers to identity providers (SAMHSA, 2020b). SAMHSA and NIAAA use information from the SAMHSA National Survey of Substance Abuse Treatment Services (N-SSATS) to describe the services offered by each provider.
Drawing from decades of research, the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), NIAAA, and SAMHSA have identified principles or “signs” of higher-quality addiction treatment programs. NIDA describes “13 principles of effective treatment,” and NIAAA and SAMHSA advise consumers to look for “five signs of higher-quality treatment (NIAAA, 2018/2020; NIDA, 2018; SAMHSA, 2018).
The goal of this study was to determine what percentage of specialty addiction treatment facilities have the attributes or signs that indicate higher quality as identified by NIDA, NIAAA, and SAMHSA, to investigate whether the percentage of facilities offering higher quality has increased over time, and to reveal how the proportions vary by state. This information will help to focus efforts to improve addiction treatment quality.
Methods
Table 1 describes the characteristics put forth by NIDA, NIAAA, and SAMHSA. These agencies identify the following as signs of higher-quality programs:
Program uses evidenced-based behavioral health therapies,
Program offers medications for addiction,
Program is accredited,
Program attends to mental health and physical health needs,
Program offers recovery support services,
Treatment is readily available when needed,
Program personalizes the treatment plan for each patient, and
Patients stay in treatment long enough and receive continuous monitoring with adjustments to the treatment plan as needed.
Data
Data were from the N-SSATS for 2007–2017 (Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality, 2018). SAMHSA conducts the N-SSATS, an annual survey of all addiction facilities in the United States. The survey collects information on facility characteristics, service modalities, specific services provided, and types and counts of clients served. SAMHSA collects the N-SSATS from all facilities in I-BHS, a census of all addiction treatment facilities in the United States that captures public and private facilities and residential, outpatient, opioid treatment programs, and detoxification programs. Response rates over the study period ranged from 89 to 95 percent of facilities. In 2017, 13,585 of 15,226 addiction facilities in the United States responded to the survey. As of 2014, SAMHSA administered an abbreviated version of the N-SSATS in even-numbered years; thus, data for the current study come from odd-numbered years.
Table 1.
43014Signs of higher-quality addiction treatment, as identified by NIDA, NIAAA, and SAMHSA
Measures
N-SSATS data captured five of the eight characteristics of higher-quality treatment described by NIDA, NIAAA, and SAMHSA. The provision of evidence-based behavioral therapies is captured in the N-SSATS questions that ask whether the facility uses the following evidence-based behavioral approaches with their patients “sometimes,” “often,” or “always”: cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), motivational interviewing (MI), 12-step facilitation, and contingency management. We interpret the facility as offering these approaches if they responded “sometimes” because the use of these services would not be appropriate for every patient (i.e., “always”). N-SSATS captures whether the facility offers addiction medications by asking whether the facility can provide methadone, buprenorphine, or naltrexone to treat opioid use disorders. We aggregate these separate questions to create a measure of whether the facility can provide at least one of these opioid use disorder medications.
Facility accreditation is captured by N-SSATS questions about whether the facility was accredited by one of the following national accrediting organizations: The Joint Commission, Commission on Accreditation of Rehabilitation Facilities, National Committee for Quality Assurance, or Council on Accreditation. Routine assessment for mental health and physical conditions and ability to treat mental health conditions is measured using N-SSATS questions on whether the facility conducts mental health assessments, offers mental health services, and tests patients for hepatitis C, HIV, and sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). We aggregated these separate questions to create a measure of whether the facility tests for all of these conditions. Whether the facility offers recovery supports and which type of supports it offers is captured by N-SSATS questions that ask whether the facility offers peer support/mentoring, self-help groups, housing assistance, employment assistance, and transportation assistance.
Analysis
We calculated national averages for each measure and percent change over 2007, 2011, and 2017. We chose 2011 because it is close to the midpoint of the study period. We could not use the exact midpoint (2012) because data on some quality signals (e.g., evidence-based behavioral therapies) were not available in that year. We characterize variation across states in 2017 using the median and range of the metrics. We also created maps to portray variation among the states in 2017.
Results
National Averages
As shown in Table 2, a greater percentage of addiction treatment facilities had attributes indicating higher quality in 2017 than in 2007. Most of the improvement occurred in the 2011–2017 period. Nonetheless, in 2017 fewer than 50 percent of facilities offered medications for opioid use disorder; testing for hepatitis C, HIV, and STDs; self-help groups; employment assistance; and transportation assistance.
Table 2.
43015National averages of signs of higher-quality addiction facilities (2007, 2011, 2017)
Note: Standard deviation in parentheses; CARF = Commission on Accreditation of Rehabilitation Facilities; COA = Council on Accreditation; JC = Joint Commission; NCQA = National Committee for Quality Assurance; OUD = opioid use disorder; STD = sexually transmitted disease.
Source: Mark et al. analysis of N-SSATS 2007–2017.
In 2017, over 90 percent of facilities reporting using CBT and MI, whereas 56 percent used contingency management. Approximately 40 percent of facilities provided medications used to treat opioid dependence (an increase from 26 percent of facilities in 2007). Roughly 51 percent of facilities were accredited in 2017. Only 18 percent of facilities screened or tested for hepatitis C, HIV, and STDs. Approximately 52 percent reported that they assess their patients for mental health comorbidities, and 68 percent reported providing mental health services. The most commonly offered recovery support service was family counseling (83 percent of facilities), followed by peer support (57 percent), housing assistance (54 percent), self-help groups (46 percent), transportation assistance (44 percent), and employment assistance (39 percent).
State Variation
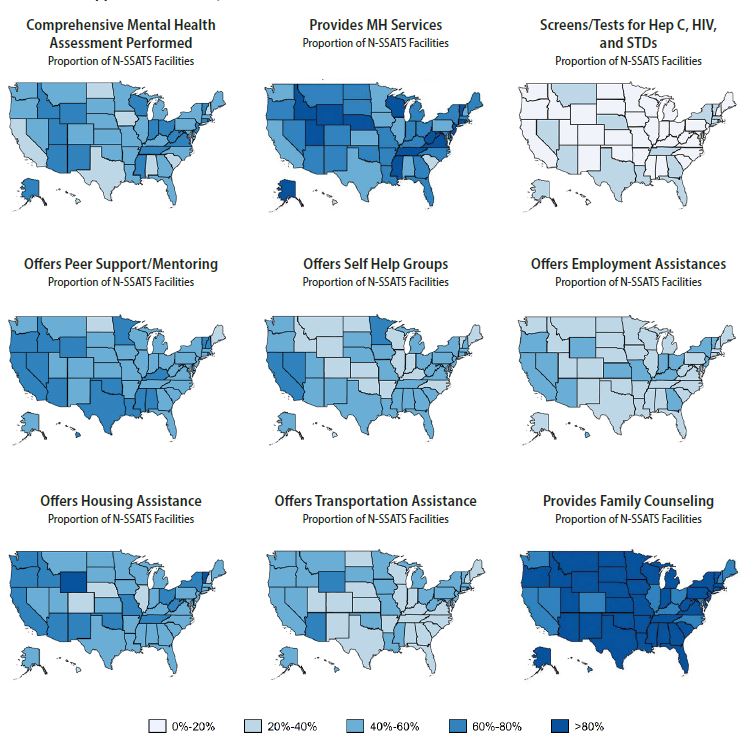
The percentage of facilities having the attributes indicating higher quality varied significantly among the states in 2017 (Table 3). CBT and MI use was high in all states, ranging from 80 to 99 percent of facilities. In contrast, the percentage of facilities within a state using 12-step facilitation ranged from 43 to 89 percent, and the percentage using contingency management ranged from 37 to 72 percent. The provision of medications for opioid use disorder ranged from 10 percent of facilities (in Hawaii) to 81 percent (in Rhode Island). The percentage of accredited facilities ranged from 15 percent (Colorado, North Dakota) to 89 percent (Alaska, Wyoming). The rate of facilities that screened for hepatitis C, HIV, and STDs ranged from 5 percent (Hawaii) to 38 percent (Nevada). The percentage range for comprehensive mental health assessments was 20 percent (Hawaii) to 74 percent (Alaska), and the percentage range for delivery of mental health services was 27 percent (Hawaii) to 96 percent (Wyoming). The proportion of facilities that offered family counseling ranged from 67 percent (Washington, DC) to 98 percent (Mississippi, Wyoming).
Table 3.
43016State variation in signs of higher-quality addiction facilities
Note: CARF = Commission on Accreditation of Rehabilitation Facilities; COA = Council on Accreditation; JC = Joint Commission; MAT = medication-assisted treatment; NCQA = National Committee for Quality Assurance; OUD = opioid use disorder; STD = sexually transmitted disease.
Source: Mark et al. analysis of National Survey of Substance Abuse Treatment Services (N-SSATS) 2017.
Figures 1 and 2 display maps of the percentage of facilities in each state having each quality characteristic in 2017. Figure 1 presents the evidence-based practices, medication, and accreditation characteristics. As noted, CBT and MI were used frequently in all states; 12-step facilitation and contingency management were more commonly used in certain regions (e.g., contingency management was used more commonly in the Southeast). Northeast states led the nation in the provision of medications to treat opioid use disorders, with over 60 percent of facilities providing medications in New Hampshire, New York, Vermont, and Rhode Island. Facilities were more likely to be accredited in the Eastern and Southcentral United States and less likely to be accredited in the upper Midwest.
Figure 2 shows the mental and physical health and recovery supports characteristics. Comprehensive mental health assessments were most common in the Southeast (i.e., Mississippi, Tennessee), Midwest (i.e., Indiana, Ohio, Wisconsin), and Mountain West (i.e., Arizona, Idaho, New Mexico, Utah, Wyoming). The provision of mental health services was highest in the Mountain West (i.e., Idaho, Utah, Wyoming) and parts of the Southeast (i.e., Mississippi, Tennessee, Virginia, West Virginia) and was lowest in some Midwestern states (i.e., Illinois, Iowa, Minnesota) and some parts of the Southeast (i.e., Alabama, South Carolina). Rates of screening for infectious diseases were low in all states.
The percentage of facilities offering recovery supports differed among the states. Southern states (i.e., Alabama, Louisiana, Mississippi, Texas) commonly offered peer support services and self-help group facilitation. Western states and diverse states like New York, Ohio, Vermont, and Wyoming frequently offered employment, housing, and transportation support. Most states offered family counseling. Data on these measures for all states for 2007, 2011, and 2017 are in an online appendix.
Figure 1.
43018State variation in signs of higher-quality addiction treatment: Evidence-based behavioral therapies, medication provision, and credentialing/accreditation, 2017
Notes: CARF = Commission on Accreditation of Rehabilitation Facilities; COA = Council on Accreditation; JC = Joint Commission; MAT = medication-assisted treatment; MH = mental health; NCQA = National Committee for Quality Assurance; N-SSATS = National Survey of Substance Abuse Treatment Services; OUD = opioid use disorder; STD = sexually transmitted disease.
Source: Mark et al. analysis of N-SSATS 2017.
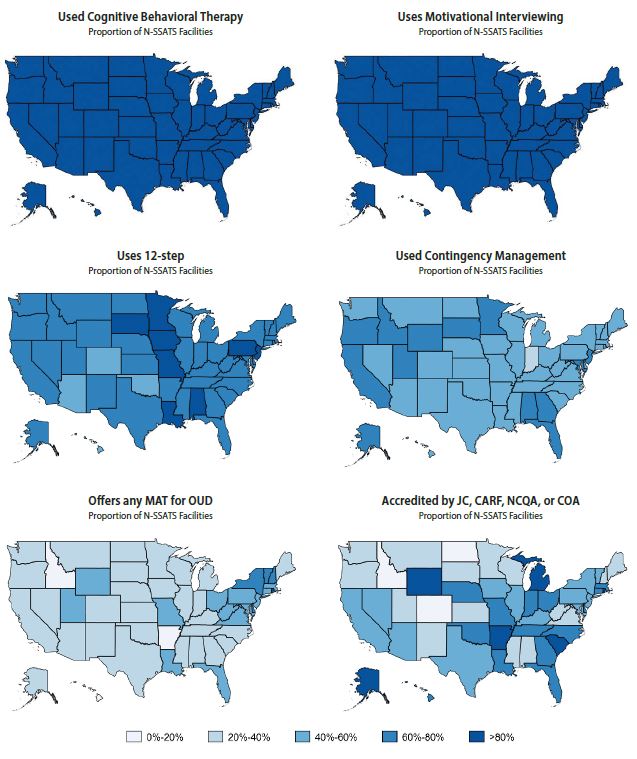
Figure 2.
43017State variation in signs of higher-quality addiction treatment: Provision of mental and physical health care and services supportive of recovery, 2017
Notes: CARF = Commission on Accreditation of Rehabilitation Facilities; COA = Council on Accreditation; JC = Joint Commission; MAT = medication-assisted treatment; MH = mental health; NCQA = National Committee for Quality Assurance; N-SSATS = National Survey of Substance Abuse Treatment Services; OUD = opioid use disorder; STD = sexually transmitted disease.
Source: Mark et al. analysis of N-SSATS 2017.
Discussion
NIDA, NIAAA, and SAMHSA have compiled signs (i.e., attributes or principles) associated with higher-quality addiction treatment. SAMHSA and NIAAA have encouraged consumers to use these to help them select among treatment providers. SAMHSA and NIAAA also offer online directories consumers can use to search for addiction treatment specialty programs. However, in 2017, approximately half or fewer of the facilities that populate these online directories offered the following services that NIDA, NIAAA, and SAMHSA consider indicative of higher-quality addiction treatment: medications for opioid use disorder; mental health assessments; testing for hepatitis C, HIV, and STDs; self-help groups; employment assistance, and transportation assistance. Moreover, consumers’ ability to find facilities that offer these services vary greatly depending on where they live.
Although the N-SSATS data have been collected by SAMHSA for many years and published in numerous peer-reviewed journal articles that describe addiction treatment programs, the data have limitations. First, N-SSATS relies on facilities to self-report information but does not verify it with secondary data sources like chart reviews. Second, the N-SSATS only captures information from specialty addiction facilities, but many individuals seek treatment outside of these specialty addiction treatment settings. The N-SSATS data exclude addiction treatment provided by independently practicing physicians, treatment in jails or prisons, and integrated care settings like primary care clinics. Third, the N-SSATS data do not capture several of the dimensions highlighted by the federal government as good practices, like rapid access to treatment, personalized treatment planning, and treatment for a sufficient time. Future efforts to capture these data elements could help improve consumers’ ability to find higher-quality treatment.
Although the signs of higher quality endorsed by NIAAA, NIAAA, and SAMHSA are grounded in research, the quantity and quality of the evidence base differ among the signs. For example, there is strong evidence from numerous randomized clinical trials that medications to treat opioid use disorders are effective in improving patient outcomes. In contrast, evidence on the association between accreditation and effectiveness is more limited. Studies find that accredited specialty addiction treatment facilities are more likely to offer medications to treat opioid and alcohol use disorders but that accredited facilities are no more likely to offer CBT (Alinsky et al., 2020; Bride et al., 2011; Knudsen et al., 2006; Knudsen & Roman, 2014). We know of no research that demonstrates patients treated in accredited addiction treatment facilities have better outcomes on average. In general, more research is needed to build the evidence base to support and refine NIH’s and SAMHSA’s principles and signs of higher-quality addiction treatment.
The characteristics of higher-quality addiction treatment programs described by the federal agencies and used in this paper are structure and process measures. Ideally, higher-quality addiction programs would be identified as providers whose patients have the best outcomes (after risk adjusting, such as for patient severity of illness at intake). The goal of addiction treatment is to reduce the symptoms of addiction like impaired functioning in social relationships and employment, excessive and dangerous substance use, and cravings. Using outcomes as a quality measure for addiction programs is particularly important because subtle (or “nonspecific”) factors that are difficult to capture in structure and process measures may be critical for the effectiveness of treatment, like an empathetic clinician–patient relationship (Wampold & Imel, 2015; Wild & Wolfe, 2009).
The limitations of the data and the measures should not overshadow the main finding of this analysis—that many facilities do not appear to offer higher-quality addiction treatment. In general, governments have leveraged both market-based and regulatory approaches to improve the quality of health care. For example, a regulatory approach would be for states to align their licensing criteria with the criteria for higher quality established by NIH and SAMHSA. The federal government has encouraged improvements in substance use disorder treatment through its Medicaid demonstration authorities, which employ both incentives and regulatory levers. The CMS Medicaid 1115 substance use disorder demonstration allows states that want to participate to receive federal matching payments for residential addiction treatment, which has historically been excluded from Medicaid if those states meet “industry standards” for higher-quality addiction treatment (CMS, 2020).
Governments could also pursue market-oriented approaches like disseminating information on which facilities have higher-quality treatment and allowing market forces to react to that information. To date, the SAMHSA and NIAAA treatment locators do not include quality metrics that empower consumers to readily identify higher-quality programs. In contrast, CMS provider locators for nursing homes, hospitals, rehabilitation facilities, psychiatric hospitals, home health programs, and hospice programs all have public-facing locators linked to quality metrics. Public-facing quality measures can drive quality improvements by giving information that allows consumers to shop based on quality and by encouraging providers to compete for patients by improving their quality. Some states, like Connecticut, have mental health and addiction facility quality dashboards that display a facility’s outcomes relative to those of its peers and to benchmarks; however, these are not meant to be public-facing tools (Connecticut Department of Mental Health and Addiction Services, 2013). The nonprofit organization Shatterproof is piloting a public-facing addiction treatment quality system. Research is needed to understand which of these approaches are most effective in promoting the quality of addiction treatment.
Substance use disorders are a leading cause of death in the United States. Treatment can reduce death rates and restore an individual’s ability to function in major life domains. However, as with other areas of health care, there are gaps between what we know works and what treatment is delivered in practice. Although NIH and SAMHSA have tried to give consumers tools to find higher-quality providers, a large portion of providers do not offer the services described as indicative of higher-quality. Multipronged federal, state, and private initiatives are needed to close these quality gaps.



